
- #Breach artifact meaning update#
- #Breach artifact meaning code#
Situational-awareness driven: enterprise risk assessments and crown jewel analysis (the identification of the digital assets that are critical to the company). Intelligence-driven - includes malware analysis, vulnerability scans, and intelligence reports and feeds. Analytics-driven: makes use of machine learning (ML) and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to develop aggregated risk scores and formulate hypotheses. This threat hunting technique involves testing three types of hypotheses: You can input the information into your SIEM using Trusted Automated eXchange of Intelligence Information ( TAXII) and Structured Threat Information eXpression ( STIX). Another great source of intelligence is the host or network artifacts provided by computer emergency response teams (CERTs), which allowyou to export automated alerts. This process can be integrated with your SIEM and threat intelligence tools, which use the intelligence to hunt for threats. You can input intelligence such as indicators of compromise, IP addresses, hash values, and domain names. Intelligence-based hunting is areactive threat hunting technique designed to react according to input sources of intelligence. Threat hunting methodologies Intelligence-based hunting 
It can be leveraged to predict trends, prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities, and improve your security measures. Whether the information is about benign or malicious activity, it can be useful in future analyses and investigations. During the resolution phase, this information is communicated to other teams and tools that can respond, prioritize, analyze, or store the information for future use. Threat hunters collect important information during the investigation phase.
#Breach artifact meaning update#
This is used to update the response plan and prevent similar attacks. Executing the incident response plan – When they detect a threat, hunters gather as much information as possible before executing the incident response plan to neutralize it.Using behavioral analysis, they can detect anomalies which could indicate a threat. Searching for hidden threats to prevent the attack from happening – Threat hunters analyze the computing environment by using constant monitoring.

#Breach artifact meaning code#
Proactively hunting for known adversaries – A known attacker is one who is listed in threat intelligence services, or whose code pattern is on the denylist of known malicious programs. 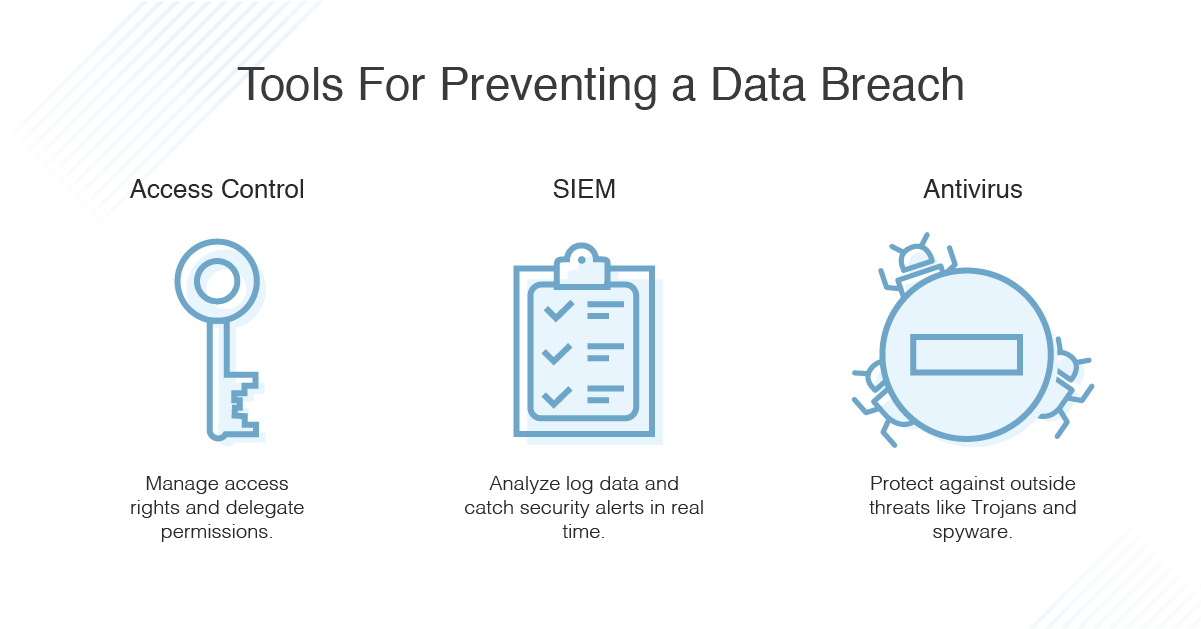 Hunting for insider threats or outside attackers – Cyber threat hunters can detect threats posed by insiders, like an employee, or outsiders, like a criminal organization. It consists of searching iteratively through networks to detect indicators of compromise (IoCs) hacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and threats such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) that are evading your existing security system. Cyber threat hunting is an active information security strategy used by security analysts.
Hunting for insider threats or outside attackers – Cyber threat hunters can detect threats posed by insiders, like an employee, or outsiders, like a criminal organization. It consists of searching iteratively through networks to detect indicators of compromise (IoCs) hacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and threats such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) that are evading your existing security system. Cyber threat hunting is an active information security strategy used by security analysts.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
